How Do the bones work?
Do you know how many bones are there in a human body? A baby is born with 300 bones, approx. 100 bones more than a full-grown adult. So what happens as you age, do you lose some bones in the process of growing? No… there are several tiny bones in a baby which fuse together to form bigger and mature bones. Bones go through various changes as human grow. 206 bones in an adult give shape to the body. In addition to protecting our organs they help us move.
TThe bones of new born babies are very soft because they are made up of flexible substance called Cartilage. As they grow, cartilage is eventually replaced by bone with the help of calcium. This replacement process is known as ossification and it is usually completed by mid-twenties. This is the time when your bones are as big and as strong as they will ever be. As you age, your bones don’t grow bigger, but they can heal and repair themselves, for example in the case of fractures.
Bones are alive; they grow and change with time.
There are four main layers of a bone:
Periosteum:
This is the outer layer of the bone containing blood vessels & nerves. It is very thin and compressed layer.
Compact:
This is the second layer giving color to the bones; comparatively it is smooth, firm, and steady. This part makes up approx. 80% of overall bone accumulation. Osteocytes make up this layer.
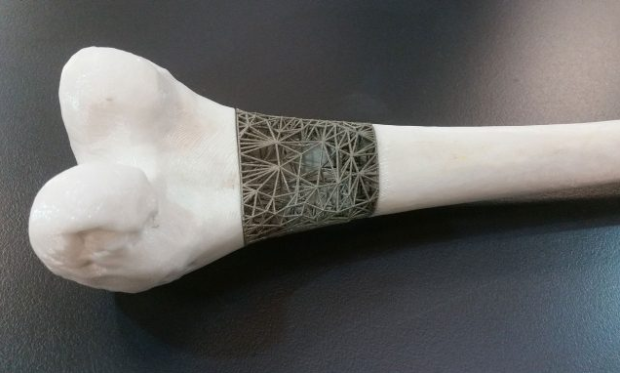
Cancellous:
The meshwork of spongy tissue (trabeculae) of mature adult bone typically found at the core of vertebral bones in the spine and the ends of the long bones (such as the femur or thigh bone). This layer comes after the compact layer; it is often called as spongy bone because it looks like a sponge. Up to 20% of the bone structure is taken by this layer.
Marrow:
Last and the most important layer of the bone is marrow. Its key function is to make new blood cells in the marrow. Everyday your bones deal with new white and red cells to control overall blood level in the body.
With aging, women’s bones lose some structure, the body slows storing of calcium and other important minerals that eventually affect your mobility and other types of functioning. Lack of calcium and other minerals like zinc, magnesium slow down the process of dead cell replacement. Your body requires more than a regular diet can possibly provide; something additional that can boost level of these nutrients in your body. 21st Reflections Collagen Peptide HyperFood has the power to deliver!